Description
External Links
#
Expression
#
Biological Properties
Transcriptome - SMDBT000914 ( APOE )
Description
- IDSMDBT000914
- Gene SymbolAPOE
- Nameapolipoprotein E
- OrganismHomo sapiens (Human)
- Gene SynonymsAD2; APO-E; ApoE4; LDLCQ5; LPG
- ChromosomeGRCh38 chr19:44905796-44909393; hg19 chr19:45409053-45412650
- Gene Sequence
CTACTCAGCCCCAGCGGAGGTGAAGGACGTCCTTCCCCAGGAGCCGTTTCTCCTTCCCCAGACTGGCCAATCACAGGCAGGAAGATGAAGGTTCTGTGGGCTGCGTTGCTGGTCACATTCCTGGCAGGATGCCAGGCCAAGGTGGAGCAAGCGGTGGAGACAGAGCCGGAGCCCGAGCTGCGCCAGCAGA Show more...
Expression
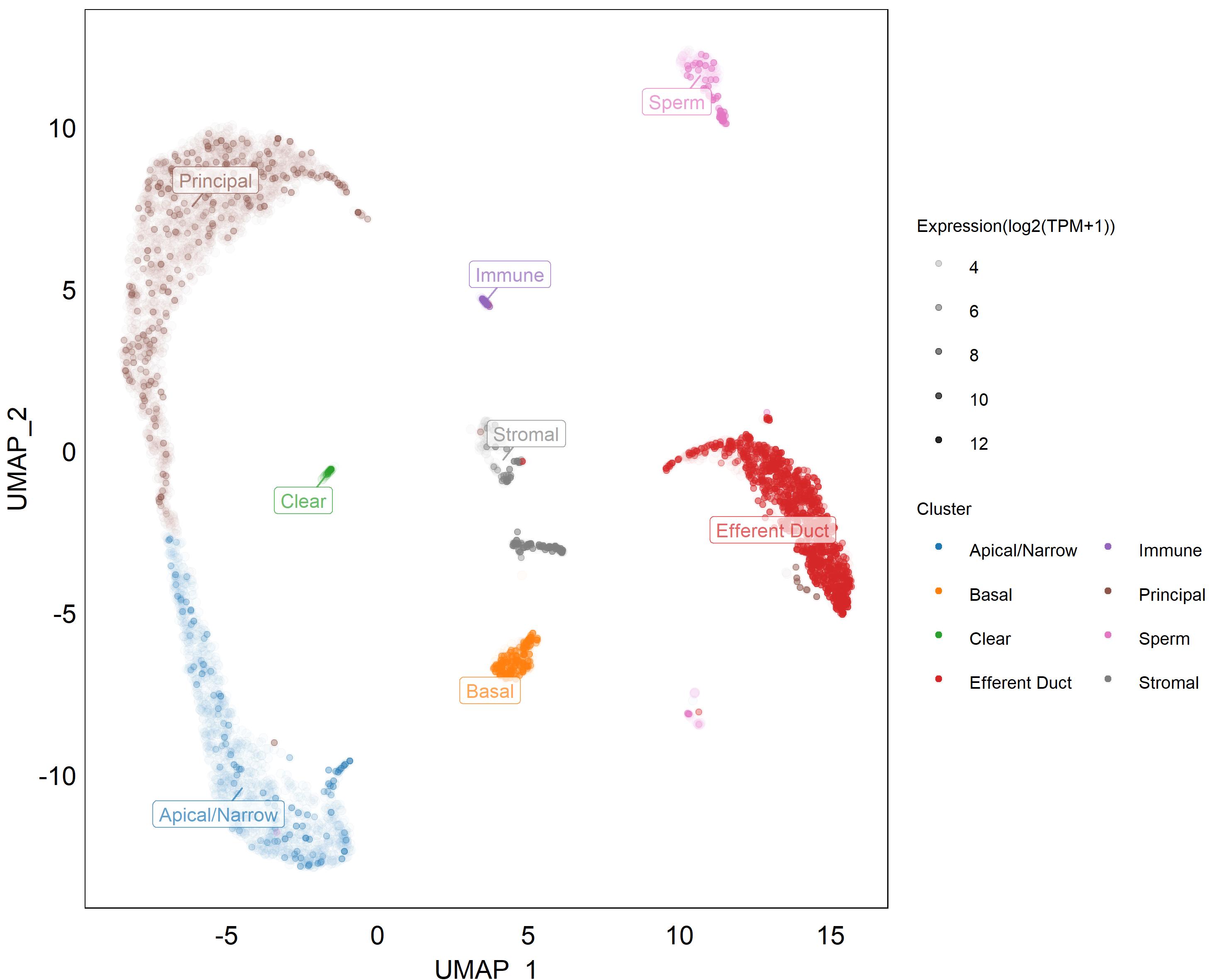
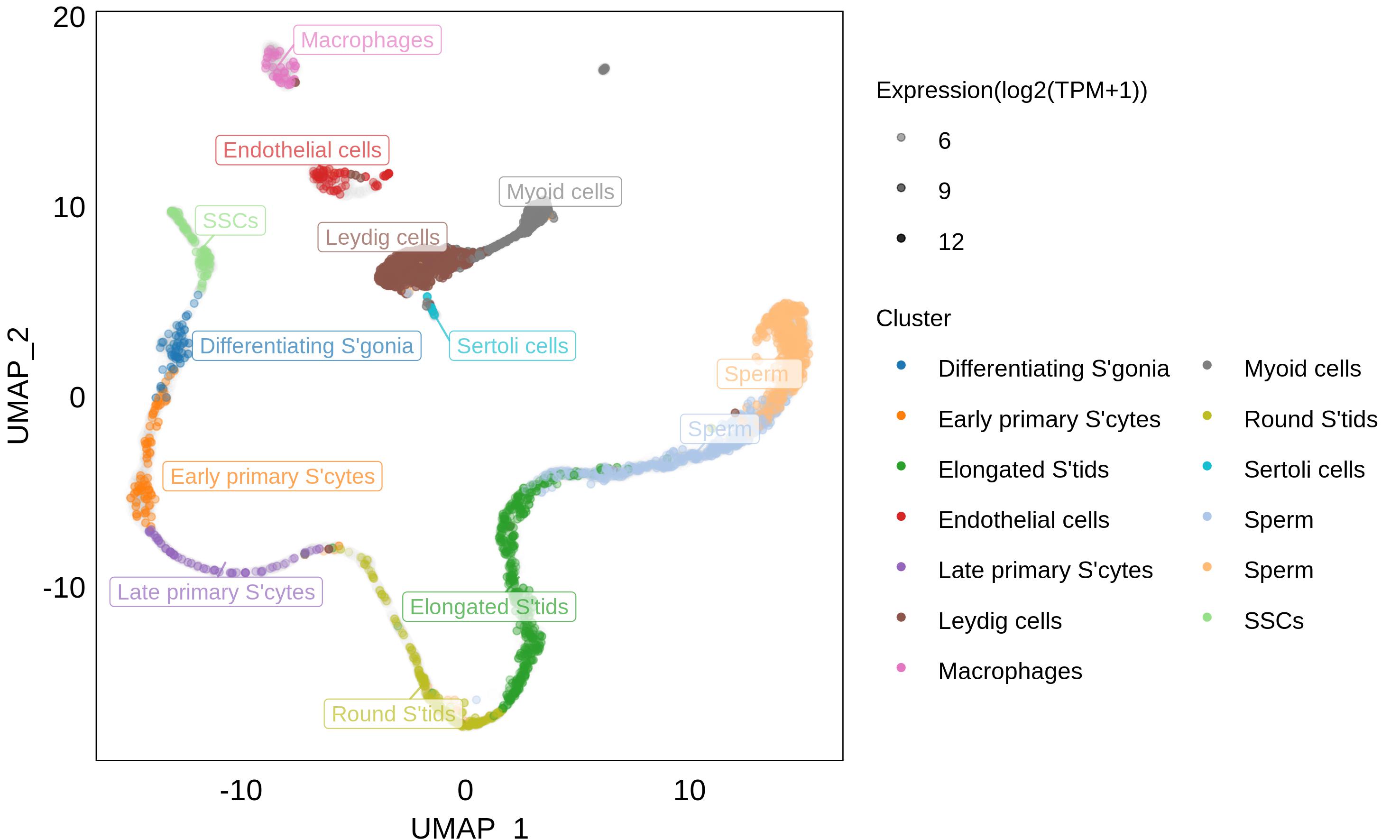
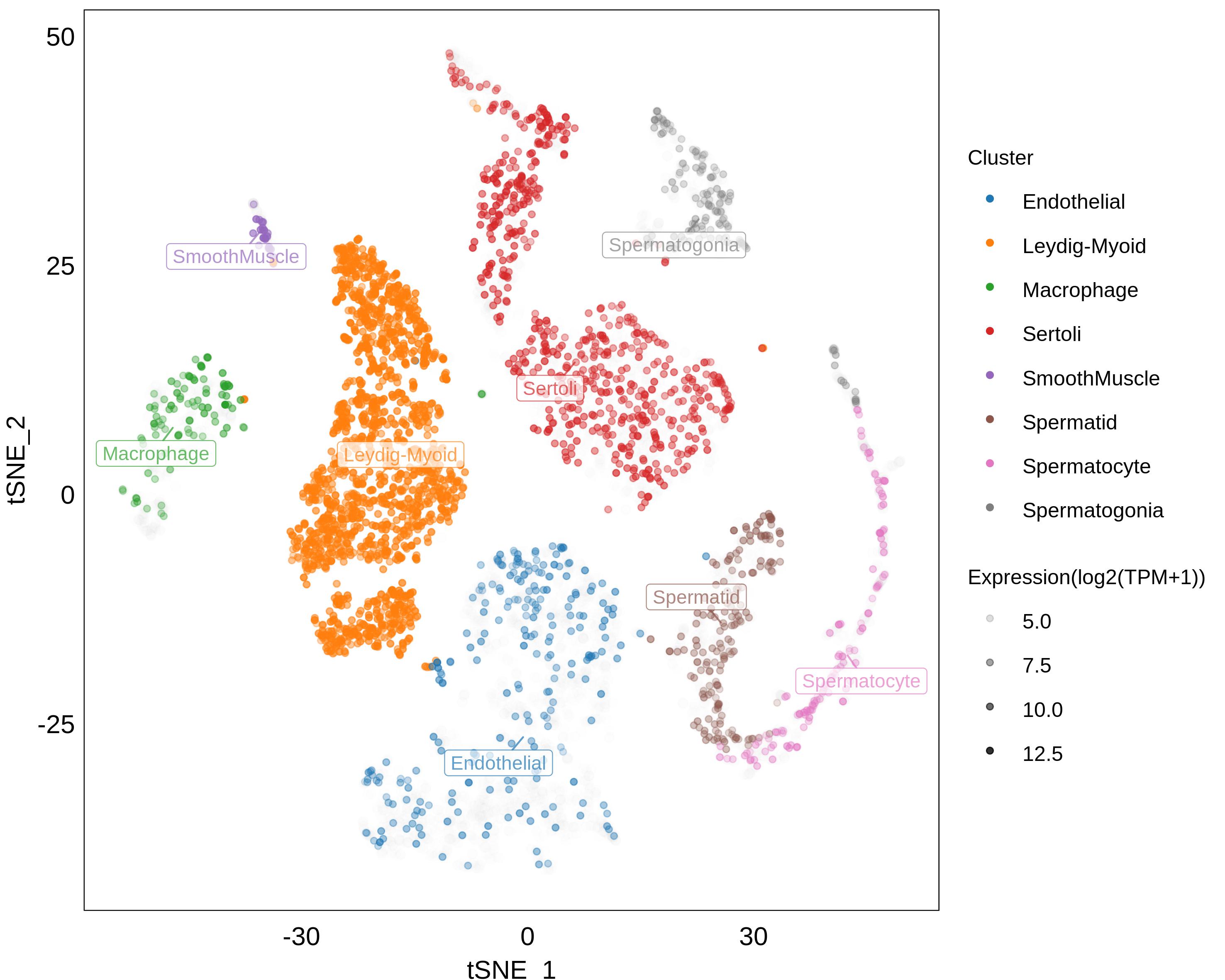
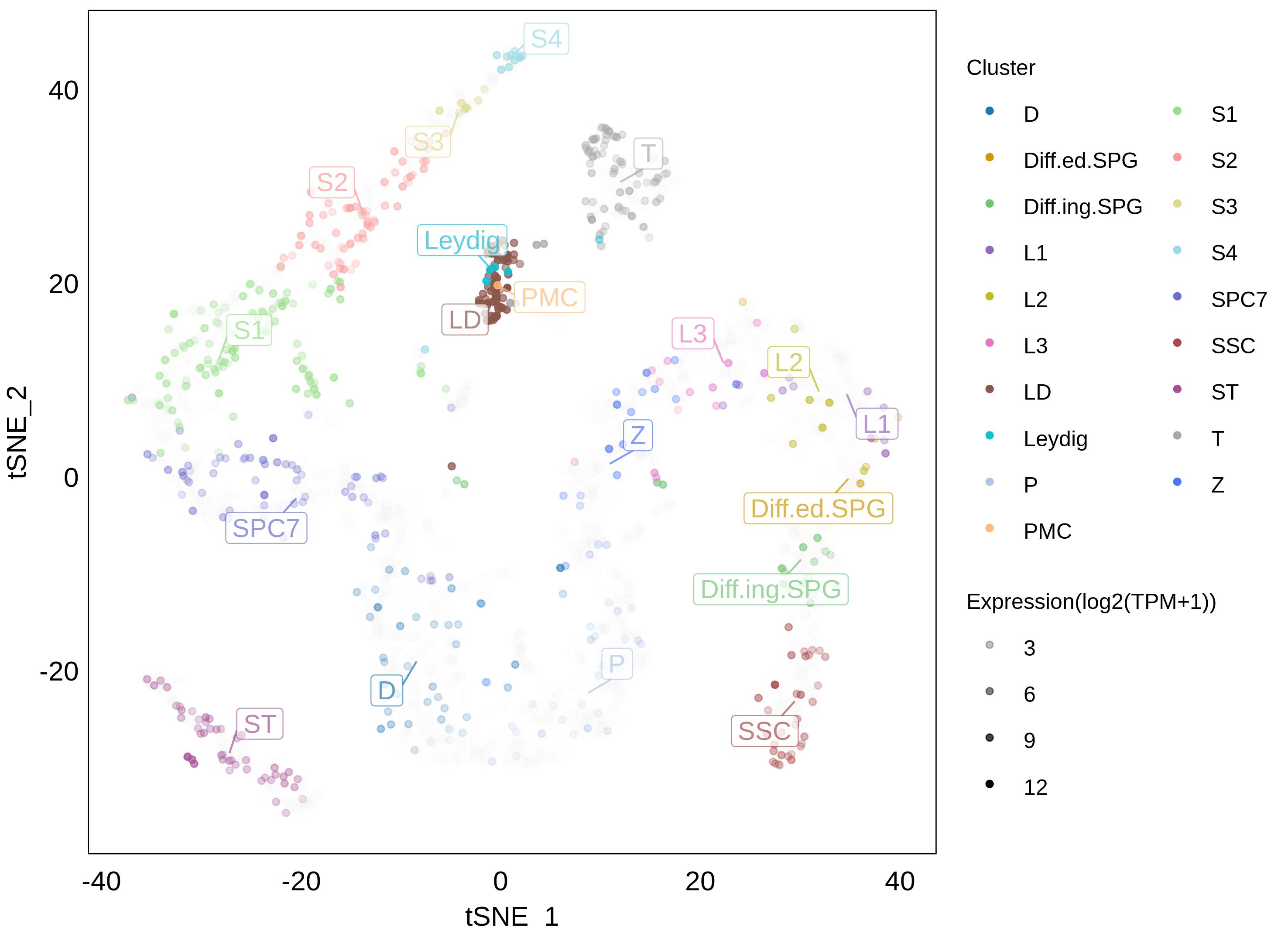
- Expression in
Tissues and Cells
Export
Biological Properties
- General FunctionAPOE is an apolipoprotein, a protein associating with lipid particles, that mainly functions in lipoprotein-mediated lipid transport between organs via the plasma and interstitial fluids (PubMed:6860692, PubMed:1911868, PubMed:14754908). APOE is a core component of plasma lipoproteins and is involved in their production, conversion and clearance (PubMed:6860692, PubMed:2762297, PubMed:1911868, PubMed:1917954, PubMed:9395455, PubMed:14754908, PubMed:23620513). Apoliproteins are amphipathic molecules that interact both with lipids of the lipoprotein particle core and the aqueous environment of the plasma (PubMed:6860692, PubMed:2762297, PubMed:9395455). As such, APOE associates with chylomicrons, chylomicron remnants, very low density lipoproteins (VLDL) and intermediate density lipoproteins (IDL) but shows a preferential binding to high-density lipoproteins (HDL) (PubMed:6860692, PubMed:1911868). It also binds a wide range of cellular receptors including the LDL receptor/LDLR, the LDL receptor-related proteins LRP1, LRP2 and LRP8 and the very low-density lipoprotein receptor/VLDLR that mediate the cellular uptake of the APOE-containing lipoprotein particles (PubMed:2762297, PubMed:1917954, PubMed:7768901, PubMed:8939961, PubMed:12950167, PubMed:20030366, PubMed:2063194, PubMed:8756331, PubMed:20303980, PubMed:1530612, PubMed:7635945). Finally, APOE has also a heparin-binding activity and binds heparan-sulfate proteoglycans on the surface of cells, a property that supports the capture and the receptor-mediated uptake of APOE-containing lipoproteins by cells (PubMed:9395455, PubMed:9488694, PubMed:23676495, PubMed:7635945). A main function of APOE is to mediate lipoprotein clearance through the uptake of chylomicrons, VLDLs, and HDLs by hepatocytes (PubMed:1911868, PubMed:1917954, PubMed:9395455, PubMed:23676495, PubMed:29516132). APOE is also involved in the biosynthesis by the liver of VLDLs as well as their uptake by peripheral tissues ensuring the delivery of triglycerides and energy storage in muscle, heart and adipose tissues (PubMed:2762297, PubMed:29516132). By participating in the lipoprotein-mediated distribution of lipids among tissues, APOE plays a critical role in plasma and tissues lipid homeostasis (PubMed:2762297, PubMed:1917954, PubMed:29516132). APOE is also involved in two steps of reverse cholesterol transport, the HDLs-mediated transport of cholesterol from peripheral tissues to the liver, and thereby plays an important role in cholesterol homeostasis (PubMed:9395455, PubMed:14754908, PubMed:23620513). First, it is functionally associated with ABCA1 in the biogenesis of HDLs in tissues (PubMed:14754908, PubMed:23620513). Second, it is enriched in circulating HDLs and mediates their uptake by hepatocytes (PubMed:9395455). APOE also plays an important role in lipid transport in the central nervous system, regulating neuron survival and sprouting (PubMed:8939961, PubMed:25173806). APOE is also involved in innate and adaptive immune responses, controlling for instance the survival of myeloid-derived suppressor cells (By similarity). Binds to the immune cell receptor LILRB4 (PubMed:30333625). APOE may also play a role in transcription regulation through a receptor-dependent and cholesterol-independent mechanism, that activates MAP3K12 and a non-canonical MAPK signal transduction pathway that results in enhanced AP-1-mediated transcription of APP (PubMed:28111074). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:P08226, ECO:0000269|PubMed:12950167, ECO:0000269|PubMed:14754908, ECO:0000269|PubMed:1530612, ECO:0000269|PubMed:1911868, ECO:0000269|PubMed:1917954, ECO:0000269|PubMed:20030366, ECO:0000269|PubMed:20303980, ECO:0000269|PubMed:2063194, ECO:0000269|PubMed:23620513, ECO:0000269|PubMed:23676495, ECO:0000269|PubMed:2762297, ECO:0000269|PubMed:28111074, ECO:0000269|PubMed:30333625, ECO:0000269|PubMed:6860692, ECO:0000269|PubMed:7635945, ECO:0000269|PubMed:7768901, ECO:0000269|PubMed:8756331, ECO:0000269|PubMed:8939961, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9395455, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9488694, ECO:0000303|PubMed:25173806, ECO:0000303|PubMed:29516132}.; (Microbial infection) Through its interaction with HCV envelope glycoprotein E2, participates in the attachment of HCV to HSPGs and other receptors (LDLr, VLDLr, and SR-B1) on the cell surface and to the assembly, maturation and infectivity of HCV viral particles (PubMed:25122793, PubMed:29695434). This interaction is probably promoted via the up-regulation of cellular autophagy by the virus (PubMed:29695434). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:25122793, ECO:0000269|PubMed:29695434}.
- GO – Biological ProcessAMPA glutamate receptor clustering [GO:0097113]; amyloid precursor protein metabolic process [GO:0042982]; artery morphogenesis [GO:0048844]; cellular calcium ion homeostasis [GO:0006874]; cGMP-mediated signaling [GO:0019934]; cholesterol catabolic process [GO:0006707]; cholesterol efflux [GO:0033344]; cholesterol homeostasis [GO:0042632]; cholesterol metabolic process [GO:0008203]; chylomicron remnant clearance [GO:0034382]; cytoskeleton organization [GO:0007010]; fatty acid homeostasis [GO:0055089]; gene expression [GO:0010467]; G protein-coupled receptor signaling pathway [GO:0007186]; high-density lipoprotein particle assembly [GO:0034380]; high-density lipoprotein particle clearance [GO:0034384]; high-density lipoprotein particle remodeling [GO:0034375]; intermediate-density lipoprotein particle clearance [GO:0071831]; intracellular transport [GO:0046907]; lipid transport involved in lipid storage [GO:0010877]; lipoprotein biosynthetic process [GO:0042158]; lipoprotein catabolic process [GO:0042159]; locomotory exploration behavior [GO:0035641]; long-chain fatty acid transport [GO:0015909]; long-term memory [GO:0007616]; low-density lipoprotein particle remodeling [GO:0034374]; maintenance of location in cell [GO:0051651]; negative regulation of amyloid-beta formation [GO:1902430]; negative regulation of amyloid fibril formation [GO:1905907]; negative regulation of blood coagulation [GO:0030195]; negative regulation of blood vessel endothelial cell migration [GO:0043537]; negative regulation of canonical Wnt signaling pathway [GO:0090090]; negative regulation of cellular protein metabolic process [GO:0032269]; negative regulation of cholesterol biosynthetic process [GO:0045541]; negative regulation of cholesterol efflux [GO:0090370]; negative regulation of dendritic spine development [GO:0061000]; negative regulation of dendritic spine maintenance [GO:1902951]; negative regulation of endothelial cell migration [GO:0010596]; negative regulation of endothelial cell proliferation [GO:0001937]; negative regulation of gene expression [GO:0010629]; negative regulation of inflammatory response [GO:0050728]; negative regulation of lipid biosynthetic process [GO:0051055]; negative regulation of lipid transport across blood-brain barrier [GO:1903001]; negative regulation of long-term synaptic potentiation [GO:1900272]; negative regulation of MAP kinase activity [GO:0043407]; negative regulation of neuron apoptotic process [GO:0043524]; negative regulation of neuron death [GO:1901215]; negative regulation of neuron projection development [GO:0010977]; negative regulation of phospholipid efflux [GO:1902999]; negative regulation of platelet activation [GO:0010544]; negative regulation of postsynaptic membrane organization [GO:1901627]; negative regulation of protein secretion [GO:0050709]; negative regulation of smooth muscle cell proliferation [GO:0048662]; negative regulation of triglyceride metabolic process [GO:0090209]; neuron projection development [GO:0031175]; nitric oxide mediated signal transduction [GO:0007263]; NMDA glutamate receptor clustering [GO:0097114]; phospholipid efflux [GO:0033700]; positive regulation by host of viral process [GO:0044794]; positive regulation of amyloid-beta clearance [GO:1900223]; positive regulation of amyloid-beta formation [GO:1902004]; positive regulation of amyloid fibril formation [GO:1905908]; positive regulation of cholesterol efflux [GO:0010875]; positive regulation of cholesterol esterification [GO:0010873]; positive regulation of dendritic spine development [GO:0060999]; positive regulation of dendritic spine maintenance [GO:1902952]; positive regulation of endocytosis [GO:0045807]; positive regulation of ERK1 and ERK2 cascade [GO:0070374]; positive regulation of heparan sulfate binding [GO:1905855]; positive regulation of heparan sulfate proteoglycan binding [GO:1905860]; positive regulation of lipid biosynthetic process [GO:0046889]; positive regulation of lipid transport across blood-brain barrier [GO:1903002]; positive regulation of low-density lipoprotein particle receptor catabolic process [GO:0032805]; positive regulation of membrane protein ectodomain proteolysis [GO:0051044]; positive regulation of neurofibrillary tangle assembly [GO:1902998]; positive regulation of neuron death [GO:1901216]; positive regulation of neuron projection development [GO:0010976]; positive regulation of nitric-oxide synthase activity [GO:0051000]; positive regulation of phospholipid efflux [GO:1902995]; positive regulation of presynaptic membrane organization [GO:1901631]; positive regulation of transcription, DNA-templated [GO:0045893]; protein import [GO:0017038]; receptor-mediated endocytosis [GO:0006898]; regulation of amyloid-beta clearance [GO:1900221]; regulation of amyloid fibril formation [GO:1905906]; regulation of amyloid precursor protein catabolic process [GO:1902991]; regulation of axon extension [GO:0030516]; regulation of behavioral fear response [GO:2000822]; regulation of Cdc42 protein signal transduction [GO:0032489]; regulation of cellular response to very-low-density lipoprotein particle stimulus [GO:1905890]; regulation of cholesterol metabolic process [GO:0090181]; regulation of innate immune response [GO:0045088]; regulation of neuronal synaptic plasticity [GO:0048168]; regulation of neuron death [GO:1901214]; regulation of proteasomal protein catabolic process [GO:0061136]; regulation of protein-containing complex assembly [GO:0043254]; regulation of protein metabolic process [GO:0051246]; regulation of tau-protein kinase activity [GO:1902947]; response to caloric restriction [GO:0061771]; response to dietary excess [GO:0002021]; response to reactive oxygen species [GO:0000302]; reverse cholesterol transport [GO:0043691]; synaptic transmission, cholinergic [GO:0007271]; triglyceride homeostasis [GO:0070328]; triglyceride metabolic process [GO:0006641]; triglyceride-rich lipoprotein particle clearance [GO:0071830]; vasodilation [GO:0042311]; very-low-density lipoprotein particle clearance [GO:0034447]; very-low-density lipoprotein particle remodeling [GO:0034372]; virion assembly [GO:0019068]
- GO – Cellular Componentblood microparticle [GO:0072562]; chylomicron [GO:0042627]; clathrin-coated endocytic vesicle membrane [GO:0030669]; collagen-containing extracellular matrix [GO:0062023]; cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; dendrite [GO:0030425]; discoidal high-density lipoprotein particle [GO:0034365]; early endosome [GO:0005769]; endocytic vesicle lumen [GO:0071682]; endoplasmic reticulum [GO:0005783]; endoplasmic reticulum lumen [GO:0005788]; extracellular exosome [GO:0070062]; extracellular matrix [GO:0031012]; extracellular region [GO:0005576]; extracellular space [GO:0005615]; extracellular vesicle [GO:1903561]; glutamatergic synapse [GO:0098978]; Golgi apparatus [GO:0005794]; high-density lipoprotein particle [GO:0034364]; intermediate-density lipoprotein particle [GO:0034363]; lipoprotein particle [GO:1990777]; low-density lipoprotein particle [GO:0034362]; membrane [GO:0016020]; neuronal cell body [GO:0043025]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; synaptic cleft [GO:0043083]; very-low-density lipoprotein particle [GO:0034361]
- GO – Molecular Functionamyloid-beta binding [GO:0001540]; antioxidant activity [GO:0016209]; cholesterol transfer activity [GO:0120020]; heparan sulfate proteoglycan binding [GO:0043395]; heparin binding [GO:0008201]; identical protein binding [GO:0042802]; lipid binding [GO:0008289]; lipid transporter activity [GO:0005319]; lipoprotein particle binding [GO:0071813]; low-density lipoprotein particle receptor binding [GO:0050750]; metal chelating activity [GO:0046911]; phosphatidylcholine-sterol O-acyltransferase activator activity [GO:0060228]; phospholipid binding [GO:0005543]; protein-containing complex binding [GO:0044877]; protein dimerization activity [GO:0046983]; protein homodimerization activity [GO:0042803]; signaling receptor binding [GO:0005102]; structural molecule activity [GO:0005198]; tau protein binding [GO:0048156]; very-low-density lipoprotein particle receptor binding [GO:0070326]