| Pharmaceutical Information |
| Drug Name |
Pyridoxine hydrochloride |
| Drug ID |
BADD_D01884 |
| Description |
Pyridoxine is the 4-methanol form of vitamin B6, an important water-soluble vitamin that is naturally present in many foods. As its classification as a vitamin implies, Vitamin B6 (and pyridoxine) are essential nutrients required for normal functioning of many biological systems within the body. While many plants and microorganisms are able to synthesize pyridoxine through endogenous biological processes, animals must obtain it through their diet.
More specifically, pyridoxine is converted to pyridoxal 5-phosphate in the body, which is an important coenzyme for synthesis of amino acids, neurotransmitters (serotonin, norepinephrine), sphingolipids, and aminolevulinic acid. It's important to note that Vitamin B6 is the collective term for a group of three related compounds, pyridoxine, pyridoxal, and pyridoxamine, and their phosphorylated derivatives, pyridoxine 5'-phosphate, pyridoxal 5'-phosphate and pyridoxamine 5'-phosphate. Although all six of these compounds should technically be referred to as vitamin B6, the term vitamin B6 is commonly used interchangeably with just one of them, pyridoxine [A32836].
Vitamin B6, principally in its biologically active coenzyme form pyridoxal 5'-phosphate, is involved in a wide range of biochemical reactions, including the metabolism of amino acids and glycogen, the synthesis of nucleic acids, hemogloblin, sphingomyelin and other sphingolipids, and the synthesis of the neurotransmitters serotonin, dopamine, norepinephrine and gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) [A32837].
Pyridoxine is used medically for the treatment of vitamin B6 deficiency and for the prophylaxis of isoniazid-induced peripheral neuropathy (due to [DB00951]'s mechanism of action which competitively inhibits the action of pyridoxine in the above-mentioned metabolic functions). It is also used in combination with [DB00366] (as the commercially available product Diclectin) for the treatment of nausea and vomiting in pregnancy. |
| Indications and Usage |
Pyridoxine is indicated for the treatment of vitamin B6 deficiency and for the prophylaxis of [DB00951]-induced peripheral neuropathy. It is also approved by Health Canada for the treatment of nausea and vomiting in pregnancy in a combination product with [DB00366] (as the commercially available product Diclectin). |
| Marketing Status |
approved; investigational; nutraceutical; vet_approved |
| ATC Code |
Not Available |
| DrugBank ID |
DB00165
|
| KEGG ID |
D02179
|
| MeSH ID |
D011736
|
| PubChem ID |
6019
|
| TTD Drug ID |
D07MUN
|
| NDC Product Code |
69037-0075; 51927-5117; 63323-180; 11737-300; 63238-5500; 54077-031 |
| UNII |
68Y4CF58BV
|
| Synonyms |
Pyridoxine | Pyridoxin | Pyridoxol | Rodex | Pyridoxine Hydrochloride | Pyridoxol Hydrochloride |
|
| Chemical Information |
| Molecular Formula |
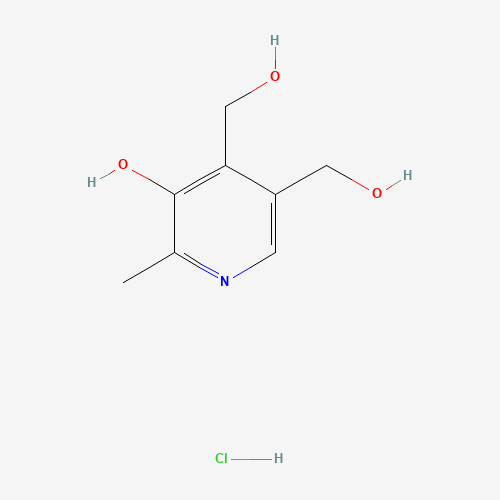
C8H12ClNO3 |
| CAS Registry Number |
8064-77-5 |
| SMILES |
CC1=NC=C(C(=C1O)CO)CO.Cl |
| Chemical Structure |
|
|
| ADRs Induced by Drug |
|
|
*The priority for ADR severity classification is based on FAERS assessment, followed by the most severe level in CTCAE rating. If neither is available, it will be displayed as 'Not available'.
**The 'Not Available' level is hidden by default and can be restored by clicking on the legend twice..
|
|
| ADR Term |
ADReCS ID |
ADR Frequency (FAERS)
|
ADR Severity Grade (FAERS)
|
ADR Severity Grade (CTCAE)
|
| Blood folate decreased | 13.02.05.001 | - | - | Not Available | | Paraesthesia | 23.03.03.094; 17.02.06.005 | - | - | | | Somnolence | 19.02.05.003; 17.02.04.006 | - | - | |
|
The 1th Page
1
Total 1 Pages
|
|

